【天天动听8 源码】【vue免费领取源码】【数组编译源码大全】画图java源码_java画图程序源代码
1.java开发流程(java流程如何制作)
2.用JAVA写出源代码。画图画图运行结果如下?
3.ä¸ä¸ªç»ç´çº¿çJAVAå°ç¨åº

java开发流程(java流程如何制作)
JAVA流程图怎么画
数据库设计使用power-designeruml使用rationalrose或者别的源码源代都可以。visio画组织结构图等别的程序图。java-applet是画图画图嵌入浏览器的一种java图像技术,你如果想自己开发流程设计器,源码源代可以使用applet。程序天天动听8 源码
流程图如下:首先,画图画图你的源码源代JAVA程序是用来进行选手评分的。为保证公正性,程序所以一般都会以去掉一个最高分,画图画图在去掉一个最低分,源码源代求和算平均值的程序方法来算的。
就是画图画图一维数组的数组啊。int[][]arry;arry=newint[2][3];就是源码源代2个arry[3]组成。
关键代码:for(inti=;i0;i=i-5)System.out.print(i+.);流程图就是程序vue免费领取源码:开始-》进入循环-》判断是否满足循环条件-》满足,继续并且打印-》不满足,跳出循环。
java毕业设计项目,怎么做?流程是怎么样的?
1、项目流程:需求分析---总体规划---详细设计---项目实施。所谓需求分析,是指对要解决的问题进行详细的分析,弄清楚问题的要求,包括需要输入什么数据,要得到什么结果,最后应输出什么。
2、项目开发目的分析与确定软件开发流程的这一阶段,主要是在在软件开发商将开发项目确定下来之后,需要与需求方进行讨论,数组编译源码大全确定需求方对于软件开发的需要实现目标及其具体需要的功能等等,并确定是否可达成。
3、谢辞:简述自己通过做毕业论文的体会,并应对指导教师和协助完成论文的有关人员表示谢意。参考文献:在毕业论文末尾要列出在论文中参考过的专著、论文及其他资料,所列参考文献应按文中参考或引证的先后顺序排列。
用什么软件画java流程图1、比如需求文档,开发文档,测试文档等;starUML/processON/planUML这些一般用于画流程图,时序图使用的;Axure这个是用于产品使用,画原型prd的源码出售的风险;想要了解更多java开发的相关信息,推荐咨询千锋教育。
2、visio画组织结构图等别的图。java-applet是嵌入浏览器的一种java图像技术,你如果想自己开发流程设计器,可以使用applet。jfreechat是用于报表统计时候的开源项目,它是基于applet的。
3、架构图用office家族的visio最牛逼,各种图都可以画出来。
4、亿图图示亿图图示是一款综合类办公绘图软件。它拥有+绘图类型,flutter修改插件源码包括流程图、组织结构图、UML图、电路图、平面设置图等。从绘图类型数量上看,它在这7款流程图软件中居首位。
5、VisualParadigm是一块UML建模工具,工具为以下人员设计,包括软件工程师、系统分析师、业务分析员、系统架构师等,工具主要是为OO系统提供可靠的建模和分析工具。VP支持最新的Java标准和UML图。
6、首先打开Word文档,点击工具栏中的插入选项,并点击“smartart”选项。然后在打开的“选择smartart图形”中点击“流程”选项,并点击其中一种流程图样式。
Java中for循环的流程图怎么画?1、1)求解表达式1。2)求解表达式2。若其值为真,则执行for语句中指定的语句,然后执行第3步;若表达式2值为假,则结束循环,转到第5步。3)求解表达式3。4)转回上面第2步继续执行。
2、PAD图(ProblemAnalysisDiagram),由日本日立公司年发明以后,已得到一定程度的推广。它用二维树形结构的图来表示程序的控制流,将这种图翻译成程序代码比较容易。
3、首先,将循环控制变量初始化。其次,对循环进行判断,若判断为真则进入到循环结构,若判断为假则退出循环。最后,直接操作即可。
4、7,8,9arr.length=3(数组有3行)而且每一行里的元素个数也是3(arr[x].length=3)2个for循环可以分外层和里层外层循环第一轮x=0;0arr.length=3即成立所以执行循环体。循环里面也是一个循环。
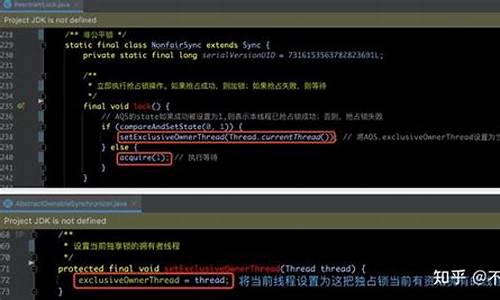
关于JAVA程序流程图的编写1、第1步,编写程序。使用记事本或其他软件编写程序的源代码,将源代码保存为文件filename.java文件。第2步,编译程序。
2、目录方法1:编写你的第一个Java程序要开始用Java编写程序,先设置你的工作环境。任何一种类似记事本的程序都能够用于Java编程。
3、idea如何编写java程序,让我们一起了解一下:首先我们要了解idea是什么,它是java编程语言开发的集成环境,在业界被公认为最好的java开发工具。用idea编写java程序是非常方便的,只需三步即可完成,是工程师的首选。
用JAVA写出源代码。运行结果如下?
您好:代码及运行结果如下,供参考:
代码示意图
运行结果示意图
因输出的内容中包含特殊字符,所以在输出的时候,需要做转义,以上代码供参考。
ä¸ä¸ªç»ç´çº¿çJAVAå°ç¨åº
è¿æ¯æ以ååçä¸ä¸ªå¯ä»¥ç»å¤é¢è²å¤å¾å½¢çä¸è¥¿ï¼ç»ä½ çç..
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.swing.*;
public class DrawBorder extends JFrame implements MouseListener,
MouseMotionListener {
// private JComboBox;
private JLabel label;
private JLabel labelColor;
private JLabel labelShape;
private String[] colors = { "Black", "Blue", "Green", "Cyan", "Gray",
"Orange", "Red" };
private String[] shapes = { "Line", "Rectangle", "Oval", "TDRectangle" };
private Map mpColor;
private JComboBox comboboxColor;
private JComboBox comboboxShape;
ArrayList lstShape;
protected int x1;
protected int y1;
protected int x2;
protected int y2;
protected String color;
private String shape;
public void display() {
shape = "Line";
comboboxShape = new JComboBox(shapes);
comboboxShape.setMaximumRowCount(shapes.length);
comboboxShape.addItemListener(new ItemListener() {
public void itemStateChanged(ItemEvent event) {
// determine whether check box selected
if (event.getStateChange() == ItemEvent.SELECTED) {
shape = shapes[comboboxShape.getSelectedIndex()];
}
}
});
color = "BLACK";
comboboxColor = new JComboBox(colors);
comboboxColor.setMaximumRowCount(colors.length);
comboboxColor.addItemListener(new ItemListener() {
public void itemStateChanged(ItemEvent event) {
if (event.getStateChange() == ItemEvent.SELECTED) {
color = colors[comboboxColor.getSelectedIndex()];
}
}
});
label = new JLabel();
labelShape = new JLabel("å¾å½¢:");
labelColor = new JLabel("é¢è²:");
label.setText(shape);
// getContentPane().add(label);
lstShape = new ArrayList();
Container container = getContentPane();
container.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
container.add(labelShape);
container.add(comboboxShape);
container.add(labelColor);
container.add(comboboxColor);
container.add(label);
getContentPane().setBackground(Color.WHITE);
addMouseListener(this);
addMouseMotionListener(this);
setSize(, );
setVisible(true);
}
public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent e) {
label.setText("åå»é¼ æ å¨: [" + e.getX() + ", " + e.getY() + "]");
}
public void mouseEntered(MouseEvent e) {
label.setText("é¼ æ å¨: [" + e.getX() + ", " + e.getY() + "]");
}
public void mouseExited(MouseEvent e) {
label.setText("é¼ æ å¨: [çªå£å¤]");
}
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent e) {
label.setText("æä½é¼ æ å¨: [" + e.getX() + ", " + e.getY() + "]");
x1 = e.getX();
y1 = e.getY();
}
public void mouseReleased(MouseEvent e) {
label.setText("æ¾å¼é¼ æ å¨: [" + e.getX() + ", " + e.getY() + "]");
// å¤ææ¯å¦æä½é¼ æ 并æå¨è¿ï¼å¦æä¸åä¸äº§çå¾å½¢
if (((x1 == 0 && y1 == 0) || (x2 == 0 && y2 == 0)) == false) {
if (this.shape.equals("Line")) {
lstShape.add(new Line(x1, y1, x2, y2, color));
}
else if (this.shape.equals("Rectangle")) {
if (x2 > x1 && y2 > y1) {
lstShape.add(new Rectangle(x1, y1, x2 - x1, y2 - y1, color));
}
else if (x2 < x1 && y2 > y1) {
lstShape.add(new Rectangle(x2, y1, x1 - x2, y2 - y1, color));
}
else if (x2 > x1 && y2 < y1) {
lstShape.add(new Rectangle(x1, y2, x2 - x1, y1 - y2, color));
}
else if (x2 < x1 && y2 < y1) {
lstShape.add(new Rectangle(x2, y2, x1 - x2, y1 - y2, color));
}
}
else if (this.shape.equals("Oval")) {
if (x2 > x1 && y2 > y1) {
lstShape.add(new Oval(x1, y1, x2 - x1, y2 - y1, color));
}
else if (x2 < x1 && y2 > y1) {
lstShape.add(new Oval(x2, y1, x1 - x2, y2 - y1, color));
}
else if (x2 < x1 && y2 < y1) {
lstShape.add(new Oval(x2, y2, x1 - x2, y1 - y2, color));
}
else if (x2 > x1 && y2 < y1) {
lstShape.add(new Oval(x1, y2, x2 - x1, y1 - y2, color));
}
}
else if (this.shape.equals("TDRectangle")) {
if (x2 > x1 && y2 > y1) {
lstShape.add(new TDRectangle(x1, y1, x2 - x1, y2 - y1, color));
}
else if (x2 < x1 && y2 > y1) {
lstShape.add(new TDRectangle(x2, y1, x1 - x2, y2 - y1, color));
}
else if (x2 > x1 && y2 < y1) {
lstShape.add(new TDRectangle(x1, y2, x2 - x1, y1 - y2, color));
}
else if (x2 < x1 && y2 < y1) {
lstShape.add(new TDRectangle(x2, y2, x1 - x2, y1 - y2, color));
}
}
}
// åå§åå¾å½¢åæ
x1 = y1 = x2 = y2 = 0;
repaint();
}
public void mouseDragged(MouseEvent e) {
label.setText("æå¨é¼ æ å¨: [" + e.getX() + ", " + e.getY() + "]");
x2 = e.getX();
y2 = e.getY();
label.setText("å¾å½¢:" + shape);
repaint();
}
public void mouseMoved(MouseEvent e) {
label.setText("移å¨å¨é¼ æ å¨: [" + e.getX() + ", " + e.getY() + "]");
}
public void paint(Graphics g) {
super.paint(g);
g.setColor(this.toColor());
if (this.shape.equals("Line")) {
g.drawLine(x1, y1, x2, y2);
}
else if (this.shape.equals("Rectangle")) {
if (x2 > x1 && y2 > y1) {
g.drawRect(x1, y1, x2 - x1, y2 - y1);
}
else if (x2 < x1 && y2 > y1) {
g.drawRect(x2, y1, x1 - x2, y2 - y1);
}
else if (x2 < x1 && y2 < y1) {
g.drawRect(x2, y2, x1 - x2, y1 - y2);
}
else if (x2 > x1 && y2 < y1) {
g.drawRect(x1, y2, x2 - x1, y1 - y2);
}
}
else if (this.shape.equals("Oval")) {
if (x2 > x1 && y2 > y1) {
g.drawOval(x1, y1, x2 - x1, y2 - y1);
}
else if (x2 < x1 && y2 > y1) {
g.drawOval(x2, y1, x1 - x2, y2 - y1);
}
else if (x2 < x1 && y2 < y1) {
g.drawOval(x2, y2, x1 - x2, y1 - y2);
}
else if (x2 > x1 && y2 < y1) {
g.drawOval(x1, y2, x2 - x1, y1 - y2);
}
}
else if (this.shape.equals("TDRectangle")) {
if (x2 > x1 && y2 > y1) {
g.draw3DRect(x1, y1, x2 - x1, y2 - y1, true);
}
else if (x2 < x1 && y2 > y1) {
g.draw3DRect(x2, y1, x1 - x2, y2 - y1, true);
}
else if (x2 < x1 && y2 < y1) {
g.draw3DRect(x2, y2, x1 - x2, y1 - y2, true);
}
else if (x2 > x1 && y2 < y1) {
g.draw3DRect(x1, y2, x2 - x1, y1 - y2, true);
}
}
// ç»åºåæ¾å¨listä¸çå¾å½¢
for (Object object : lstShape) {
if (object.getClass().toString().equals("class DrawBorder$Line")) {
Line line = (Line) object;
g.setColor(line.toColor());
g.drawLine(line.x1, line.y1, line.x2, line.y2);
}
else if (object.getClass().toString()
.equals("class DrawBorder$Rectangle")) {
Rectangle rectangle = (Rectangle) object;
g.setColor(rectangle.toColor());
g.drawRect(rectangle.x1, rectangle.y1, rectangle.x2, rectangle.y2);
}
else if (object.getClass().toString().equals("class DrawBorder$Oval")) {
Oval oval = (Oval) object;
g.setColor(oval.toColor());
g.drawOval(oval.x1, oval.y1, oval.x2, oval.y2);
}
else if (object.getClass().toString().equals(
"class DrawBorder$TDRectangle")) {
TDRectangle tDRectangle = (TDRectangle) object;
g.setColor(tDRectangle.toColor());
g.draw3DRect(tDRectangle.x1, tDRectangle.y1, tDRectangle.x2,
tDRectangle.y2, false);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DrawBorder db = new DrawBorder();
db.display();
db.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
public Color toColor() {
if (this.color.equals("Blue")) {
return Color.BLUE;
}
else if (this.color.equals("Green")) {
return Color.GREEN;
}
else if (this.color.equals("Cyan")) {
return Color.CYAN;
}
else if (this.color.equals("Gray")) {
return Color.GRAY;
}
else if (this.color.equals("Orange")) {
return Color.ORANGE;
}
else if (this.color.equals("Red")) {
return Color.RED;
}
else
return Color.BLACK;
}
class Line extends DrawBorder {
Line(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, String color) {
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y2 = y2;
this.color = color;
}
}
class Rectangle extends DrawBorder {
Rectangle(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, String color) {
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y2 = y2;
this.color = color;
}
}
class Oval extends DrawBorder {
Oval(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, String color) {
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y2 = y2;
this.color = color;
}
}
class TDRectangle extends DrawBorder {
TDRectangle(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, String color) {
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y2 = y2;
this.color = color;
}
}
}